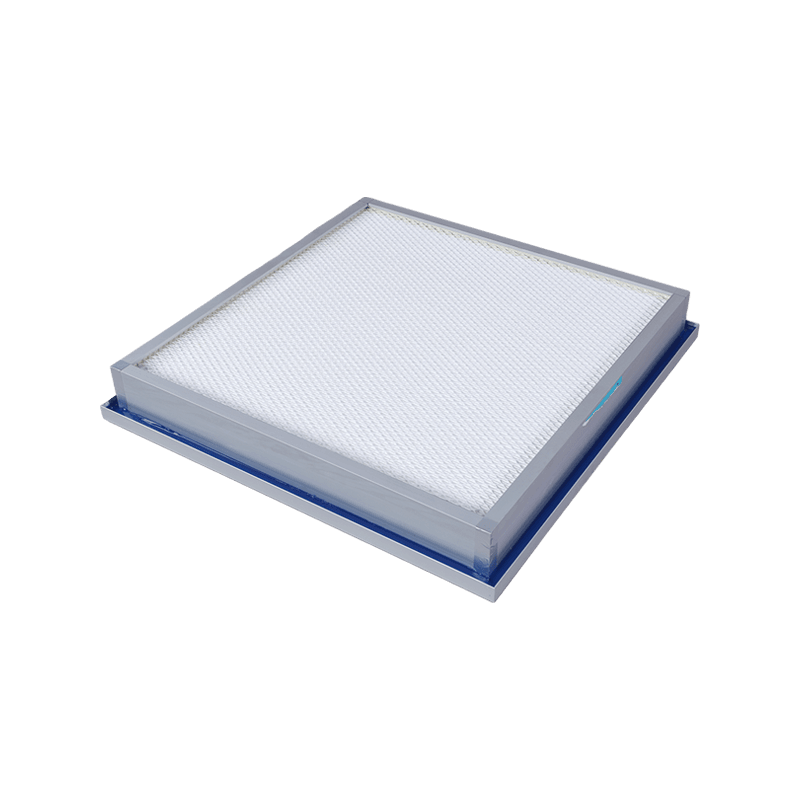
How tight is the air filter for clean rooms?The tightness of the
air filter for clean rooms is one of the key factors in its performance because it directly affects the filtration efficiency and the environmental control of the clean room. Here are some features regarding air filter sealing for cleanroom applications:
1. Filter frame: Filters are usually installed in specially designed frames or housings that ensure a tight seal between the filter and the cleanroom wall or ceiling.
2. Gaskets: Use gaskets (such as rubber or silicone gaskets) between the filter frame and the clean room structure to prevent unfiltered air from bypassing the filter and entering the clean room.
3. Filter interface: The filter interface is designed to ensure tightness with the duct system or air handling unit (AHU) of the clean room to prevent air leakage.
4. Filter material: The filter material should have good sealing properties to prevent particles from leaking through the pores of the filter material.
5. Filter pleats: The pleat design inside the filter can increase the filtering area and help improve sealing because the contact between the pleats is closer.
6. Filter support grid: A support grid is used inside the filter to maintain the shape and structure of the filter material and prevent the filter from deforming under high pressure, thereby affecting the sealing.
7. Regular inspection and maintenance: In order to ensure the sealing of the filter, it is necessary to regularly check the integrity of the filter frame, sealing gasket and filter itself, and replace damaged parts in a timely manner.
8. Installation quality: A professional installation team should ensure that the filter is installed correctly and the sealing gasket is placed correctly to achieve the best sealing effect.
9. System design: The air filtration system design of the entire clean room should take into account sealing, including the location, number and air flow path of filters.
What is the structure of an air filter for clean rooms?The structural design of an
air filter for clean room is critical to its performance. Here are some common structural features:
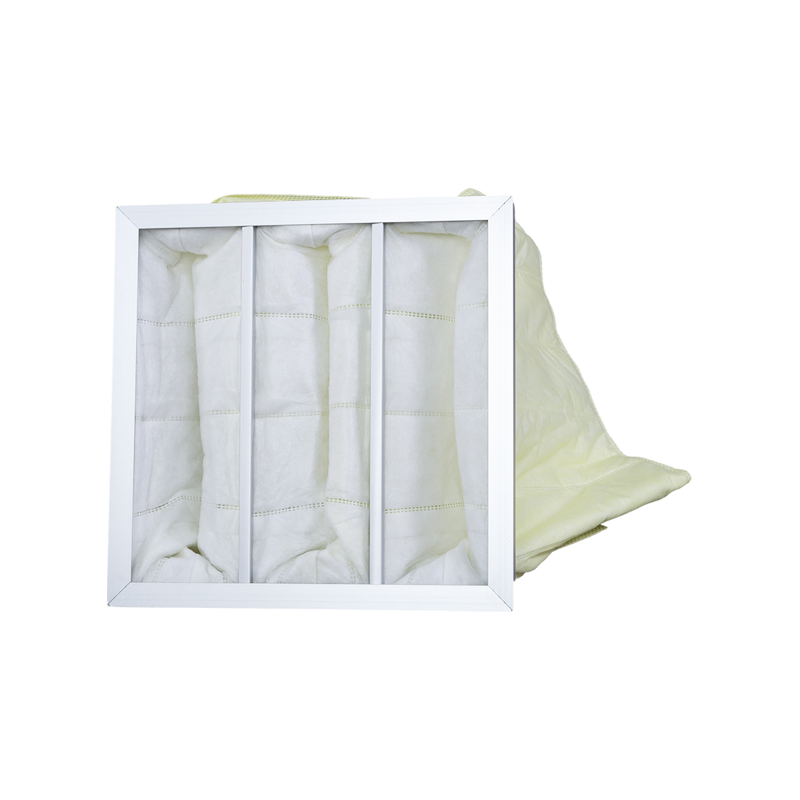
1. Filter Frame: Filters are typically mounted in a sturdy metal or plastic frame to provide structural support and protect the filter material. Frames can be disposable or reusable.
2. Filter material: The filter material is the core part of the filter and is usually made of synthetic fibers such as polyester, polypropylene or fiberglass. These materials have high filtration efficiency and low resistance.
3. Pleated design: Filter materials are usually arranged in V-shaped, wavy or parallel pleats to increase the filtration area and improve filtration efficiency while reducing the volume and weight of the filter.
4. Support grid: There are usually support grids on both sides of the filter material to maintain the shape and structure of the filter and prevent deformation under high pressure.
5. Gasket: The edge of the filter frame is usually equipped with a gasket to ensure the seal between the filter and the clean room wall, ceiling or air handling unit.
6. Protective nets: Protective nets may be installed on the inlet and outlet sides of the filter material to prevent large particles from directly impacting the filter material and extend the service life of the filter.
7. Filter interface: Filters usually have standardized interfaces, such as flanges or slots, to facilitate installation and replacement.
8. Directional markings: There are usually directional markings on the filter to ensure correct installation and prevent reverse air flow.
9. Filter level: Depending on the filtration efficiency, filters may be divided into different levels, such as primary efficiency, medium efficiency, high efficiency particulate air (HEPA) and ultra high efficiency particulate air (ULPA).
10. Size: The size of the filter can be customized according to the size and air flow needs of the clean room.
11. Special designs: For specific applications, filters may have special designs, such as electrostatic charging treatment, antibacterial treatment, or chemical filtration capabilities.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español 简体中文
简体中文